Tricot – using a crowdsourced citizen science approach for variety testing at scale
Purpose
Make variety testing easier and more informative for breeders, farmers, processors and consumers.
Expected impact
Tricot provides more and better data, making it possible to test varieties at scale with farmers and consumers. Tricot is easy to involve partner organizations, such as extension services, NGOs, and farmer organizations. As a result, plant breeders and seed system managers have better information to improve their product advancement decisions, from plant selection to variety release and seed marketing. Farmers gain access to varieties that match the local growing conditions, market demand and consumer preferences.
Description of the approach
Tricot tests options (such as crop varieties) with users following a crowdsourced citizen science strategy, supported by digital media. Tricot is faster than conventional testing, because:
- Digital support: the ClimMob platform streamlines data management while QR codes avoid mistakes.
- Simple tasks: each participant only evaluates three items, making it is easier to evaluate varieties, communicate with participants and collect data.
- Robust data collection: participants rank items, a simple and accurate way to gather data.
- Representativeness: participants use their own crop management strategy or cooking technique.
- Standardization: standardized approaches facilitate scaling and pooling data across trials.
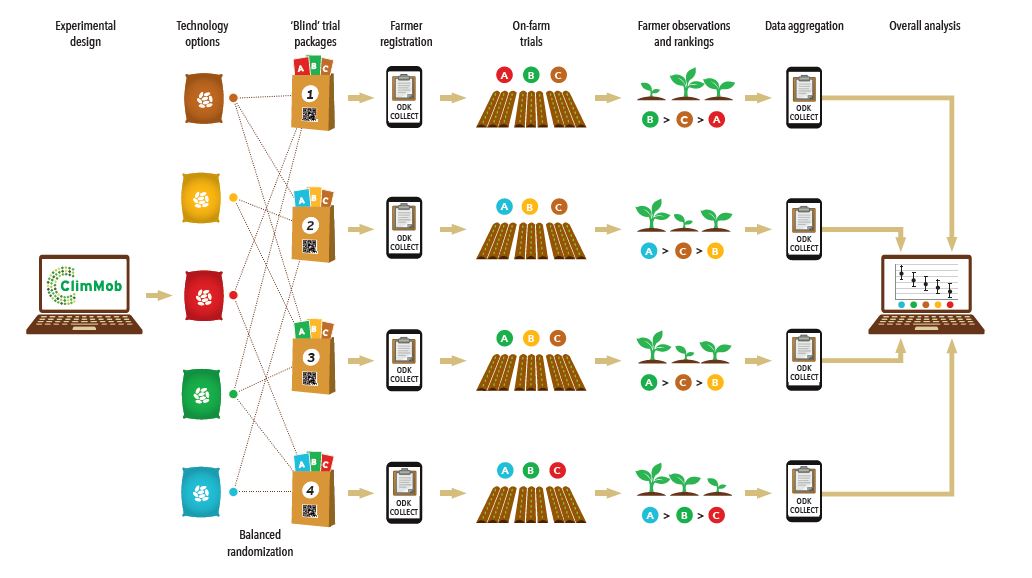
Overview of the tricot process. Testers get packages with three technology options, randomly assigned to them. Trial design, data collection and data analysis are digitally supported by the ClimMob platform.
Examples of use
Consumer testing of sweetpotato varieties in Uganda and Ghana, by the International Potato Center and local partners.
On-farm testing of RTB varieties in Ghana (sweetpotato), Rwanda (potato, cassava), Nigeria (cassava), and Uganda (cassava) by the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) and others.
Testing of many non-RTB crops in other countries.
Several NARS and NGOs are testing tricot to decide about its adoption as the main variety testing approach, including Savanna Agricultural Research Institute (SARI) in Ghana and the National Root Crop Research Institute (NRCRI) in Nigeria.
Links to relevant online resources
New Approaches to Breed More Roots, Tubers and Banana Crop Varieties
Contact persons
Jacob van Etten j.vanetten@cgiar.org








